Castellation
This step prepares you for fitting the mesh to the geometric model. Refine the mesh by splitting the hexahedral cells. The refinement of the mesh is controlled by the size level, which uses the base grid size as a baseline of 0, and then splits the hexahedron into four for every increment of 1. Isolate the mesh by checking if the base mesh intersects the geometry, and then remove the cells outside the geometric boundaries.

There are two options: Configuration and Advance. The mesh refinement can be set for Surface/Feature or Volume.
Configuration
Number of Cells between Levels

Rapid changes in cell size are not good for the mesh system, which is why we have a buffer zone when changing levels. The figure below shows the results when the size level of the circle is 1, 2, and 3.
This value is applied to castellatedMeshControls.nCellsBetweenLevels in snappyHexMeshDict file.
Feature Angle Threshold
If the angle formed by the normal of two neighboring surface is greater than this value, the maximum level of surface refinement for a given surface is used. The figure below shows the results of mesh refinement based on the feature angle threshold when there are two hexahedra and the size level of the inner hexahedron is given a minimum level of 1 and a maximum level of 2.
This value is applied to castellatedMeshControls.resolveFeatureAngle in snappyHexMeshDict file

Keep Non-Manifold Edges
This option is used when extracting feature edges of surfaces and is an option to include edges with three or more connected faces.
Keep Open Edges
This option is used when extracting feature edges for surfaces, and determines whether edges with only one connected face should be included.
Advanced
Max. Global Cell Count
The number of cells after refinement and before removing the cells of outside domain. Cell refinement stops when this value is reached as a limit on the total number of cells.
This value is applied to castellatedMeshControls.maxGlobalCells in snappyHexMeshDict file
Max. Local Cell Count
The maximum number of cells on each core in parallel computation. Parallel computations use ‘refinement-followed-by balancing’, and when this value is reached, the ‘weighted balancing method’ is used. This can result in slower speeds.
This value is applied to castellatedMeshControls.maxLocalCells in snappyHexMeshDict file.
Min. Refinement Cell count
You may have a problem where the mesh refinement process is consuming a lot of time because of a small number of cells. Stop the mesh refinement process when the remaining cells reach the value specified here. This setting is to prevent the mesh refinement process from spending too much time on a small number of unimportant cells.
This value is applied to castellatedMeshControls.minRefinementCells in snappyHexMeshDict file.
Max. Load Unbalance
The relative difference in the number of cells per process in parallel computation. Lower values result in more frequent load balancing, while higher values can disable load balancing.
This value is applied to castellatedMeshControls.maxLoadUnbalance in snappyHexMeshDict file
Allow Free Standing Zone Faces
This should be set to true when the faceZone is an independent face, such as a baffle.
This value is applied to castellatedMeshControls.allowFreeStandingZoneFaces in snappyHexMeshDict file
Surface/Feature Refinement
Click the (+) on the right to create them.
Specify the level for each surface and feature and select the surfaces to apply. Surfaces are those created in [1.Geometry]. Surface Refinement can give a minimum and maximum level. If the angle formed by the normals of two adjacent surface is greater than the value entered in the ‘Feature Angle Threshold’, the maximum level is used; otherwise, the minimum level is used.
You do not need to select feature lines as they are created by baramMesh when you create the geometry.
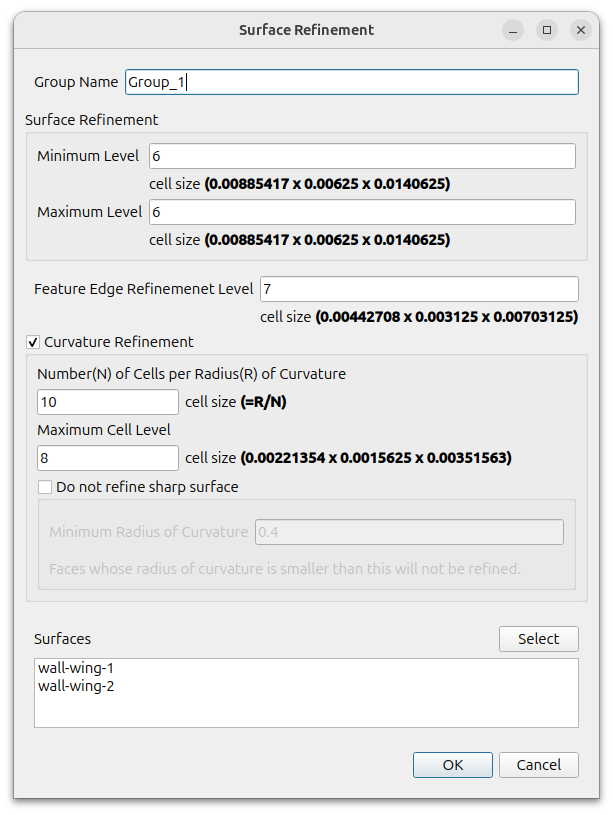
Curvature Refinement
BaramMesh has a [Feature Angle Threshold] feature as a way to adjust mesh refine level on a Surface. This is a way to densify the mesh where two surfaces form a sharp angle. In addition, we have added a way to vary the refinement level based on the curvature of the surface. You adjust the size of the mesh on curved surface by specifying [Number of cells per Radius of Curvature]. This is useful for densifying mesh where there is curvature, such as the leading edge of an airplane wing, without having to specify a separate region.
Use 3 inputs as below
- Number of cells per Radius of Curvature : If the input value is N and the radius of curvature is R, then the mesh size will be R over N
- Maximum Cell Level : Limit the maximum level to prevent too many cells
- Do not refine sharp surface option : This option prevents excessive cells in areas that are very small relative to the total. When using this option, enter [Minimum Radius of Curvature] and do not apply it if it is smaller than that.
The image below shows this applied to the front of the airfoil. On the right is the application.
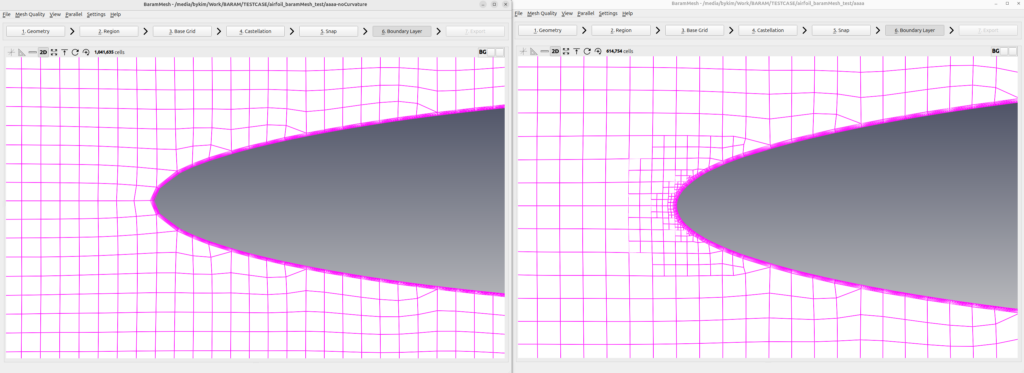
It does not apply to areas where the mesh will be split by the [Feature Angle Threshold]. The left side of the illustration below shows curvature refinement set but not applied when the feature angle threshold is 30. The middle image is with curvature refinement applied with a feature angle threshold of 100. The right image is with no curvature refinement set and a feature angle threshold of 30, with the maximum level of surface increased to 3.
Volume Refinement
Specify the level for each volume and select the volumes to apply. Volumes are those created in [1.Geometry]

Gap Refinement
The Gap Refinement option automatically refine the mesh into closely spaced areas. This can be handy if you have multiple surfaces that are very close together, or if you have thin plates or wings. There are five inputs
- Min. Cell Layers in a gap : Enter an integer greater than 3 as the minimum number of mesh to fit in the narrow gap.
- Gap detection start level : Here, gap refinement is applied if the gap is smaller than the mesh size for a given level.
- Max. refinement level : Do not apply levels greater than this value.
- Direction : Inside is an option that applies to narrow gaps inside closed faces, refine the mesh in the direction of the thickness of a thin plate or wing. Outside applies to gaps between surfaces and other surfaces. Mixed applies both inside and outside.
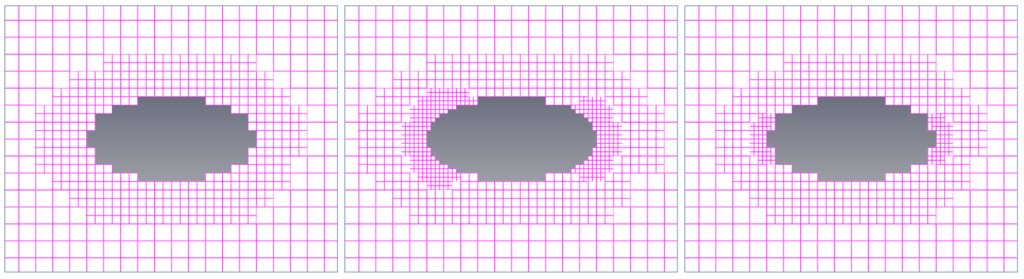
- Include surface’s own gap : Choose whether to apply to surface’s own gap. In the image below, the left side is not included and the right side is included.

Directional Level Increment
When creating a mesh, this feature allows you to refine the mesh in only one or two directions: x,y,z. It does not specify a separate level, but rather determines how much to increase an existing level.
- Number of increment level per direction
- Input for each x, y, and z direction. The value given here will be added to the existing value to create the level.
- Max/Min Value
- Applies only to the mesh of levels from minimum to maximum.