Installation and Start
Installation
Visit the installation instructions for BARAM-v24.
https://baramcfd.org/installation
BARAM-v24 is available in the Microsoft Azure cloud with no installation required. It is available by accessing the following sites
Start
On Windows, BaramFlow and BaramMesh icons are created on the desktop after the program installation is complete. Double-click the icons to run them.
On Linux, use the terminal to run the file. In the terminal, navigate to the folder where BARAM is installed and run the file to start the program. The executable file is a bash script and the command is as follows.
- BaramFlow : bash baramFlow.sh
- BaramMesh : bash baramMesh.sh
When you run BARAM, a window appears where you can choose whether to run a new calculation or open an existing problem.

Start Window
The window displays the folders that have been recently solved, which you can select to start BARAM and open the problem. If you want to open an existing case and it is not displayed in the window, you can select the folder by pressing the Open button.
To start a new calculation, click the New Case button and enter the name in the desired location, then the Solver Type, Multiphase Model selection window will appear, and then BARAM will be executed.

New Case
Solver Type
The solver type is selected between Pressure-based and Density-based.

Solver Type setup
The Density-based solver is a solver for analyzing transonic/supersonic flows with shock waves, where the velocity of the flow is higher than the speed of sound. Transonic/supersonic flows require techniques to reliably compute the rapid changes in flow variables such as pressure, density, and temperature before and after the shock wave. These techniques are currently only available in \textit{TSLAeroFoam}, the density-based solver in Baram. In Baram v6, the pressure-based solver PCNFoam had this capability, but this solver is not supported in v24 and is planned to be included in the future.
TSLAeroFoam is currently only capable of steady-state calculations, and transient analysis is planned.
For subsonic compressible flows without shock waves, density-based solvers are less convergent at lower Mach numbers, so it is better to use pressure-based solvers.
Pressure-based should be chosen for chemical species mixing and multiphase flow simulations.
Multiphase Model
For multiphase flow models, choose between Off and Volume of Fluid. If more than two phases are present, select Volme of Fluid.

Multiphase Model setup
Main Window
When you run the program, you'll see a window of figure below.

Main window
The main window can be divided into five areas
- Menu
- Graphics Toolbar
- Navigation
- Select items such as Models, Materials, Boundary Conditions, Numerical Conditions, Initial Conditions
- Configration
- Setup conditions such as Models, Materials, Boundary Conditions, Numerical Conditions, Initial Conditions
- Graphics \& Console
- Console : shows residuals, messages, error statements and more as the calculation progresses
- Mesh : show mesh
- Residuals : show residuals graph as the calculation progresses
- Monitor : show graphs of monitoring values as the calculation progresses
Menu
Th Menu consists of File, Mesh, View, Parallel, Settings, External Tools and Help.
File
Save
Save all settings.
Save As
Save all settings under a different name, but not the calculation results.
Load Mesh
Import a mesh. The following grid file formats are supported.
- openfoam : Select either the constant or polyMesh folder. For multiregion problems, you should select the constant folder because there are multiple polyMesh folders. If you select a specific polyMesh folder in the grid of a multiregion problem, only that part of the grid will be read.
- Fluent : Convert msh and cas file. Only ASCII files are supported. It uses the fluenToFoam utility developed by NEXTFoam and can convert to a multiregion mesh and polyhedral mesh. If you select a file with more than one cellzone, the window shown in the following figure appears (it does not appear when there is only one cellzone). The name of each cellzone appears, and you can select which region it is and whether it is fluid or solid. You can add a region by clicking the (+) icon or delete a region by clicking the trash can icon.
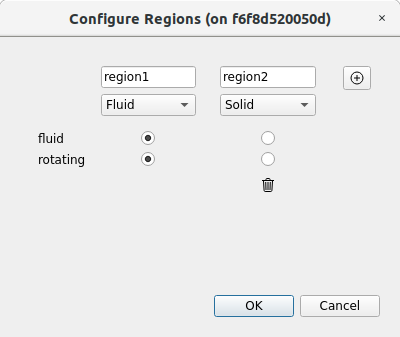
fluent mesh convert window
- StarCCM+ : StarCCM+ : Convert ccm file. Requires the libccmio library to be present. Supported on Linux only.
- Gmsh : Converts msh files from Gmsh, an open source lattice generation program. Only ASCII files are supported.
- I-deas Universal : I-deas Universal : Convert unv files. Only ASCII files are supported.
Close Case
Close the current task and returns to the initial screen of BaramFlow (select New Case or Open).
Exit
Exit program.
Mesh
show grid information and Scale/Translate/Rotate mesh.
- Mesh Info. : show mesh information and domain size
- Scale : input x, y, z scale ratio
- Translate : input translate distance of x, y, z direction
- Rotate : input rotation center, axis and angle
View
On/Off Console, Mesh, Residual, Monitor window.
Parallel

Parallel setup window
Make settings for parallel computation. Select the number of CPU cores and parallel computation method. There are Local Machine and Cluster, and in the case of Cluster, you need a text file with the node list. The View/Edit button lets you type directly or load a file. The contents of the file are as follows:
[node name1] cpu=[number of cores]
[node name2] cpu=[number of cores]
[node name3] cpu=[number of cores]
...
Settings
There are 3 items as Scale, Language, ParaView.
- Scale : This adjusts the program's resolution, and anything higher than the default of 1.0 will result in larger windows and larger text. You must close and restart the program for the new settings to take effect.
- Language : Currently, only English, Suomi (Finnish), and Korean are supported. Language translation is done using Qt Linguist. Anyone can contribute translations. https://baramcfd.org/docs/internationalization
- ParaView : Specifies the location of the ParaView executable.
External Tools
External Tools has You can find program information and third party program information in About. ParaView entry, which drives ParaView for post-processing.
Help
External Tools has a ParaView entry, which drives ParaView for post-processing.

About window

third party software information
Graphics Toolbar
The toolbar for three-dimensional graphics has the icons shown in the figure.

graphics tool bar
 Axis : Show axis at (0, 0, 0)
Axis : Show axis at (0, 0, 0)
 Axis Grid : Show axis coordinates of whole domain
Axis Grid : Show axis coordinates of whole domain
 Ruler : Show the distance between two points on the boundary surface
Ruler : Show the distance between two points on the boundary surface
 Perspective : Select the Perspective/Orthogonal method
Perspective : Select the Perspective/Orthogonal method
 Fit : Fit the size of displayed model
Fit : Fit the size of displayed model
 Axis View : Set view point to axis normal closest to the current state
Axis View : Set view point to axis normal closest to the current state
 Rotation View : Rotate 90 degrees
Rotation View : Rotate 90 degrees
 Display Options : Select mesh display method
Display Options : Select mesh display method
 Backgroud Color : Set background color
Backgroud Color : Set background color
Mouse Control
- Rotation : Press the left mouse button and Move
- Translation : Press the mouse wheel and Move
- Scale : Rotate the mouse wheel or press the right mouse button and Move
- Select Boundary : click the left mouse button - selected boundary turns white